Simple and extensible static site generator written in Python.
- simplicity
- extensibility
- live update (changes are visible in browser right after saving the file)
- jinja2 templates
- front matter markdown
pip install staticpieNote: At least Python 3.8 version is required.
pie create website mywebsitepie create page anotherpageThe pages are editable front matter markdown files. That means the pages are divided into two parts:
- metadata part written in YAML
- content part written in Markdown
Both parts are separated by ---.
To edit page open the *.md file in any text file editor and run:
pie serve -c mywebsite/mywebsite.yamlThe command will generate the website in public folder (given in config file), run http server and open the website in browser.
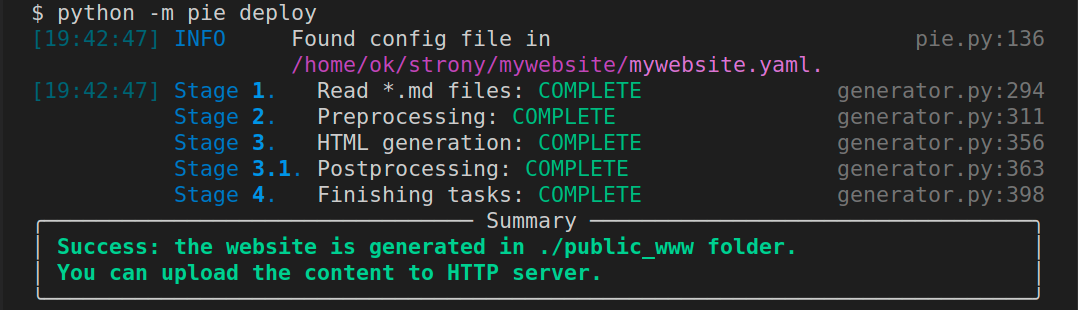
After successfull execution of serve you should see screen similar to below:
Once the file is saved, the browser refreshes the website (or some parts of it).
The serve action generates the website for localhost. That means it replaces all the addresses to localhost. The deploy option should be used to generate website with parameters given in yaml config file:
pie deploy The configuration is a YAML file and contains following elements:
PUBLIC_FOLDER- where the website should be deployed (or served)BASE_URL- the website domainPROTOCOL-http://orhttps://includes- list of files that should be copied to public folder (css, js, imgs)extensions- list of extensions (elements) used on website- and other elements (such as extension configs, etc.)
# deployment folder
PUBLIC_FOLDER: ./public_www
# the URL used for deploy
BASE_URL: www.example.com
# the protocol http:// or https://
PROTOCOL: http://
# Folders/files that should be copied to public folder
includes:
- assets
- styles.css
- styles.rtl.css
# Extensions
extensions:
- menu
- tags
- pagelist
- search
- mostrecent
# Extension config
tags:
tags_ignored:
- movie
tags_map:
art:
label: Article # the `art` tag will be displayed as Article
order: 100
art2:
label: Annother article category
order: 101Most of the parts of this engine is written as extension.
Writing a custom extension is straightforward and can be described in a few steps:
-
Create a python (
*.py) file in theextensionsfolder inside the root webside folder. It can be also a folder with a*.pyfile of the same name. Example:mywebsite +- mywebsite.yaml +- extensions +- myextension.py # 1st way +- anotherext # 2nd way +- __init__.py +- anotherext.py +- ... -
The extension file (i.e.
myextension.py) contains a class that inherits fromExtensionclass. Example:from pie.core.extension import Extension class Myextension(Extension): ...
-
Finally, the
Myextensionclass implements at least one of the following methods:on_generation_start,preprocessing,postprocessing,on_generation_end.
The details can be found in
pie.core.extension.Extensionclass.
Note: This project was created only for my use case and I suggest using some popular widely used frameworks such as Hugo or Jekyll for production.