cemirutils is a Python utility library designed to provide a range of commonly used functions, methods, libraries, and decorators to streamline development in Linux and Python environments.
- Python 3.9 or higher
pip install -U cemirutils- Cem Emir Yüksektepe (@gmail.com) https://cem.pw
- Muslu Yüksektepe (@gmail.com) https://muslu.org
- Hasan Yüksektepe (@gmail.com) https://hayatikodla.net
- Doğancan Avcı (@gmail.com) https://dogancan.me
- Ali Alın (@gmail.com) https://alilinux.com
- Methods:
loop: Decorator to measure loop execution time.check_loop: Context manager for loop timing.
- Methods:
condition_collector: Decorator to log the lines and conditions met during function execution.
- Methods:
notify: Sends an email notification after the function execution.
- Methods:
get_methods: Returns available HTTP methods.get: Executes a GET request.post: Executes a POST request.put: Executes a PUT request.delete: Executes a DELETE request.patch: Executes a PATCH request.
- Methods:
timeit: Measures execution time.log: Logs function calls and results.retry: Retries a function upon failure.cache: Caches function results.cache_with_expiry: Caches results with an expiry time.deprecate: Marks a function as deprecated.debug: Logs detailed function calls.before_after: Executes actions before and after function calls.rate_limit: Limits function calls over a period.webhook_request: Sends a webhook request on function call.
- Methods:
send_email: Sends an email with optional attachments.
- Methods:
create_sqlite_db: Creates SQLite DB from CSV.get_ip_location: Retrieves IP location data.
- Methods:
psql_create_table: Creates a PostgreSQL table.psql_insert: Inserts data into a table.insert: Inserts data.read: Reads data from a table.update: Updates table data.delete: Deletes data from a table.
-
Methods for File Operations:
linux_ls: Lists files in a directory.linux_touch: Creates a new file.linux_gzip: Compresses a file.linux_cat: Displays file content.linux_cp: Copies a file.linux_mv: Moves a file.linux_rm: Deletes a file.linux_mkdir: Creates a new directory.linux_rmdir: Removes an empty directory.linux_cut: Cuts fields from a file.linux_find: Searches for files.linux_grep: Searches text in a file.
-
Methods for List Operations:
list_head: Returns the first N elements.list_tail: Returns the last N elements.list_main: Returns the middle elements.list_unique_values: Returns unique values.list_sort_asc: Sorts the list in ascending order.list_sort_desc: Sorts the list in descending order.list_filter_greater_than: Filters values greater than a given number.list_filter_less_than: Filters values less than a given number.list_sum_values: Sums the values.list_average: Calculates the average.list_flatten: Flattens a nested list.list_multiply_by_scalar: Multiplies each element by a scalar.list_get_max_value: Returns the maximum value.list_get_frequency: Returns the frequency of a value.
-
Methods for Dictionary Operations:
dict_get_keys: Returns the keys.dict_filter_by_key: Filters by key.dict_merge: Merges dictionaries.
-
Methods for Time Operations:
time_days_between_dates: Returns days between dates.time_hours_minutes_seconds_between_times: Returns hours, minutes, and seconds between times.time_until_date: Returns time until a date.time_add_days_and_format: Adds days to a date and formats it.time_is_weekend: Checks if a date is a weekend.time_is_leap_year: Checks if a year is a leap year.time_days_in_month: Returns days in a month.time_next_weekday: Returns the next weekday.time_since: Returns the time since a date.time_business_days_between_dates: Returns business days between dates.
This documentation provides an overview of the CemirUtils classes and their respective functions, offering a range of utilities for file operations, HTTP requests, email handling, PostgreSQL operations, and more.
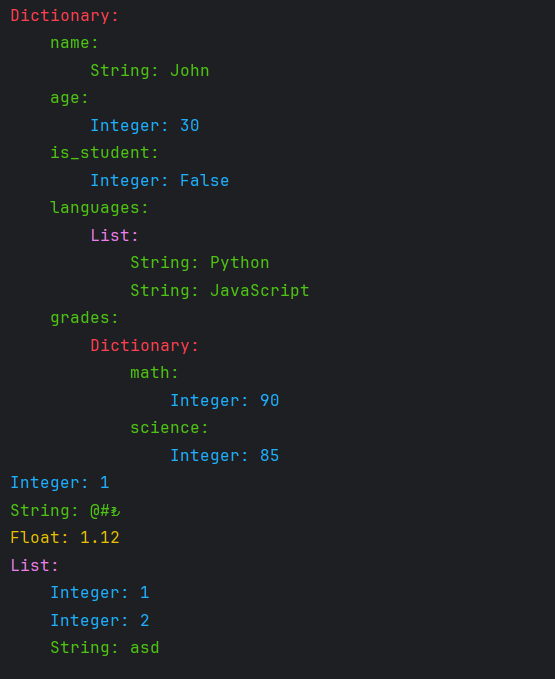
from cemirutils import cprint
data = {
"name": "John",
"age": 30,
"is_student": False,
"languages": ["Python", "JavaScript"],
"grades": {
"math": 90,
"science": 85
}
}
cprint(data)
cprint(1)
cprint("@#₺")
cprint(1.12)
cprint([1,2,"asd"])from cemirutils import crange
# Kullanım örneği / Example usage
for i in crange(1, '99-105', 'c,e,m,i,r'):
print(i)
# Output:
# 1
# 99
# 100
# 101
# 102
# 103
# 104
# 105
# c
# e
# m
# i
# rimport time
from cemirutils import CemirUtilsLoopTimer
timer = CemirUtilsLoopTimer()
@timer.loop
def example_function():
with timer.check_loop():
for _ in range(10):
time.sleep(0.1)
with timer.check_loop():
count = 0
while count < 3:
count += 1
time.sleep(count)
with timer.check_loop():
for _ in range(5):
time.sleep(0.1)
example_function()
# Output:
# String: ------------------
# String: Loop 1 (For at line 4): 1.09 seconds
# String: Loop 2 (While at line 9): 6.04 seconds
# String: Loop 3 (For at line 15): 0.54 seconds
# String: Total execution time of 'example_function': 7.68 seconds
# String: ------------------
from cemirutils import CemirUtilsConditions
cemir_utils = CemirUtilsConditions()
@cemir_utils.condition_collector
def test_function(x, y, z):
if x > 15:
# print("x is greater than 15")
pass
elif x < 15 and y > 10:
# print("x is less than 15 and y is greater than 10")
pass
else:
# print("x is not within the expected range or y is not greater than 10")
pass
if y == 20:
# print("y is exactly 20")
pass
elif y >= 15:
# print("y is greater than or equal to 15")
pass
else:
# print("y is less than 15")
pass
if z == "hello":
# print("z is 'hello'")
pass
elif z == "world":
# print("z is 'world'")
pass
else:
# print("z is something else")
pass
if x == 10:
# print("x is 10")
pass
elif x >= 10:
# print("x is greater than or equal to 10")
pass
else:
# print("x is less than 10")
pass
if y % 2 == 0:
# print("y is even")
pass
else:
# print("y is odd")
pass
if z.startswith("hq"):
# print("z starts with 'h'")
pass
elif z.startswith("w"):
# print("z starts with 'w'")
pass
else:
# print("z starts with another letter")
pass
test_function(10, 20, "hello")
# Output:
# x is less than 15 and y is greater than 10
# y is exactly 20
# z is 'hello'
# x is 10
# y is even
# z starts with another letter
# Line 10: elif x < 15 and y > 10:
# Line 15: if y == 20:
# Line 22: if z == "hello":
# Line 29: if x == 10:
# Line 36: if y % 2 == 0:
# Line 45: else:from cemirutils import CemirUtilsFunctionNotification
utils = CemirUtilsFunctionNotification(
smtp_server="mail.makdos.com",
smtp_port=587,
smtp_user="notify@makdos.com",
smtp_password="nope"
)
@utils.notify(to_email="musluyuksektepe@gmail.com", subject="Function Called")
def important_action():
return {"status": "Important action completed."}
# SMTP server must be working
important_action()from cemirutils import CemirUtilsHTTP
http = CemirUtilsHTTP()
# Show methods name
print(http.get_methods())
get_response = http.get("https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/1", verify_ssl=True)
print("GET Response:", get_response)
# POST
post_data = {"title": "foo", "body": "bar", "userId": 1}
post_response = http.post("https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts", data=post_data, verify_ssl=True)
print("POST Response:", post_response)
# PUT
put_data = {"title": "foo", "body": "bar", "userId": 1}
put_response = http.put("https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/1", data=put_data, verify_ssl=True)
print("PUT Response:", put_response)
# DELETE
delete_response = http.delete("https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/1", verify_ssl=True)
print("DELETE Response:", delete_response)
# PATCH
patch_data = {"title": "foo"}
patch_response = http.patch("https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/1", data=patch_data, verify_ssl=True)
print("PATCH Response:", patch_response)import time
from datetime import datetime
from cemirutils import CemirUtilsDecorators
@CemirUtilsDecorators.timeit
@CemirUtilsDecorators.log
def timeit_log(x, y):
time.sleep(1)
return x + y
timeit_log(3, 5)
# Output:
# Calling function 'timeit_log' with arguments (3, 5) and keyword arguments {}
# Function 'timeit_log' returned 8
# Function 'timeit_log' took 1.0018 seconds
@CemirUtilsDecorators.retry(retries=5, delay=2)
def may_fail_function():
if time.time() % 2 < 1:
raise ValueError("Random failure!")
return "Success"
may_fail_function()
# Output:
# Attempt 1 failed: Random failure!
# Attempt 2 failed: Random failure!
# Attempt 3 failed: Random failure!
# Attempt 4 failed: Random failure!
# Attempt 5 failed: Random failure!
# Function 'may_fail_function' failed after 5 attempts
@CemirUtilsDecorators.cache
def slow_function(x):
time.sleep(2) # Performing a time-consuming operation.
return x * x
print(slow_function(4))
print(slow_function(4)) # This time, result will be fetched from cache
# Output:
# 16
# Returning cached result for slow_function with args (4,) and kwargs {}
# 16
@CemirUtilsDecorators.cache_with_expiry(expiry_time=5)
def cached_function(x):
time.sleep(3) # Performing a time-consuming operation as an example.
return x * x
print(datetime.now(), cached_function(4))
time.sleep(1)
print(datetime.now(), cached_function(4)) # Time has expired, so it will be recalculated
# Output:
# 2024-06-17 13:02:29.906200 16
# Returning cached result for cached_function with args (4,) and kwargs {}
# 2024-06-17 13:02:33.920453 16
@CemirUtilsDecorators.deprecate("Please use new_function instead.")
def old_function(x, y):
return x + y
old_function(3, 5)
# Output:
# WARNING: old_function is deprecated. Please use new_function instead.
@CemirUtilsDecorators.debug
def add_numbers(a, b):
return a + b
add_numbers(3, 5)
# Output:
# DEBUG: Calling function 'add_numbers' with arguments (3, 5) and keyword arguments {}
# DEBUG: Function 'add_numbers' returned 8
@CemirUtilsDecorators.before_after
def test_beforeafter(data):
print(f"1 Performing database operation with data: {data}")
return "2 Success"
print(test_beforeafter("Muslu Y."))
# Output:
# Starting transaction
# 1 Performing database operation with data: Muslu Y.
# Committing transaction
# 2 Success
# max_call = Specifies how many times a function can be called within a certain period of time.
# period = For example, when set to period=10, the function can be called 5 times within a 10-second period.
@CemirUtilsDecorators.rate_limit(max_calls=5, period=10)
def limited_function():
return {"status": "ok"}
# Test the rate-limited function
try:
print(datetime.now(), limited_function())
print(datetime.now(), limited_function())
print(datetime.now(), limited_function())
time.sleep(4)
print(datetime.now(), limited_function()) # This call should succeed
print(datetime.now(), limited_function())
print(datetime.now(), limited_function())
print(datetime.now(), limited_function()) # This call should raise a rate limit error
except RuntimeError as e:
print(e)
#Output:
# 2024-06-17 13:19:42.270686 {'status': 'ok'}
# 2024-06-17 13:19:42.270686 {'status': 'ok'}
# 2024-06-17 13:19:42.270686 {'status': 'ok'}
# 2024-06-17 13:19:46.281105 {'status': 'ok'}
# 2024-06-17 13:19:46.281105 {'status': 'ok'}
# Rate limit exceeded
utils = CemirUtilsDecorators()
@utils.webhook_request(url="https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts", headers={"x-sent-by": "CemirUtils", "user-agent": "CemirUtils"})
def send_webhook():
return {'message': 'Webhook request'}
print(send_webhook())
@CemirUtilsDecorators.webhook_request(url="https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts", headers={"x-sent-by": "CemirUtils", "user-agent": "CemirUtils"})
def send_webhook():
return {'message': 'Webhook request'}
print(send_webhook())
from cemirutils import CemirUtilsEmail
# Kullanım
email_util = CemirUtilsEmail(
smtp_host="smtp.gmail.com",
smtp_port=465,
smtp_user="musluyuksektepe@gmail.com",
smtp_pass="nopass",
smtp_ssl=True
)
email_util.send_email(
to_email="cememir2017@gmail.com",
subject="Test Subject",
body_html="<html><body><h1>This is a test email in HTML.</h1></body></html>",
attachments=["2024.pdf", "not_found.log"],
zip_files=False # ZIP if files are exist
)from cemirutils import IPGeolocation
ip_geolocator = IPGeolocation()
## CSV -> SQLite
# ip_geolocator.create_sqlite_db()
#
ip_address = "121.0.11.0"
location_info = ip_geolocator.get_ip_location(ip_address, force_download=False)
print(location_info)from datetime import datetime
from cemirutils import CemirPostgreSQL
utils = CemirPostgreSQL(dbname='test_db3', dbhost='127.0.0.1', dbuser='postgres', dbpassword='', dbport=5435, dbcreate_db_if_not_exists=True)
# print(utils.psql_create_table('test_table_flat', 'id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY, name VARCHAR(100), surname VARCHAR(100)'))
# print(utils.psql_create_table('test_table_json', 'id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY, dates DATE, content JSONB'))
# print(utils.psql_insert('test_table_flat', ('id', 'name', 'surname'), (3, 'Muslu', 'Yüksektepe'), get_id=True))
print(utils.insert('test_table_json', ('id', 'dates', 'content'), (2, datetime.now(), {"age": 40, "city": "İzmir"}), get_id=True))
print(utils.read('test_table_json'))
print(utils.update('test_table_json', {'dates': datetime.now(), 'content': '{"age": 40, "city": "Sivas"}'}, 'id = 1', get_id=True))
print(utils.read('test_table_json'))
asd = utils.read(table_name='test_table_json', columns="content", condition="content ->> 'age' = '40'")
# asd = utils.read(table_name='test_table_json', columns="content", condition="content ->> 'age' like '%4%'")
print(type(asd), asd)
# asdd = Dict2Dot(asd[0])
# print(type(asd), asdd.id)
print(utils.delete('test_table_json', 'id = 1'))
print(utils.read('test_table_json'))from cemirutils import CemirUtils
utils = CemirUtils()
# Sample usage of file operations
files = utils.linux_ls(path=".")
print(files)
utils.linux_touch(file_name="new_file.txt")
utils.linux_gzip(file_name="file.txt")
content = utils.linux_cat(file_name="file.txt")
print(content)
utils.linux_cp(src="file.txt", dest="copy_file.txt")
utils.linux_mv(src="file.txt", dest="moved_file.txt")
utils.linux_rm(file_name="file.txt")
utils.linux_mkdir(dir_name="new_dir")
utils.linux_rmdir(dir_name="new_dir")
utils.linux_cut(file_name="file.txt", delimiter=" ", fields=[1, 2])
utils.linux_find(path=".", name="*.txt")
utils.linux_grep(file_name="file.txt", pattern="search_text")from cemirutils import CemirUtils
data_list = [3, 1, 4, 1, 5, 9, 2, 6, 5, 3, 5]
cem = CemirUtils(data_list)
print(data_list)
print(cem.list_head(2)) # Prints the first 2 elements of the list.
print(cem.list_tail(4)) # Prints the last 4 elements of the list.
print(cem.list_main()) # Prints the middle elements of the list.
print(cem.list_unique_values()) # Prints the unique elements of the list.
print(cem.list_sort_asc()) # Prints the list in ascending order.
print(cem.list_sort_desc()) # Prints the list in descending order.
print(cem.list_filter_greater_than(5)) # Prints values greater than 5: [9, 6]
print(cem.list_filter_less_than(4)) # Prints values less than 4: [3, 1, 1, 2, 3]
print(cem.list_sum_values()) # Prints the sum of values: 44
print(cem.list_average()) # Prints the average of values: 4.0data = [{'a': 1}, {'b': 2}, {'a': 3}, {"name": "sivas", "age": 10}]
cemd = CemirUtils(data)
print(cemd.dict_get_keys())
print(cemd.dict_filter_by_key('name'))
print(cemd.dict_merge({'a': 1}, {'b': 2}))from cemirutils import CemirUtils
utils = CemirUtils(None)
print(utils.time_days_between_dates("2024-05-01", "2024-05-25")) # 24
print(utils.time_hours_minutes_seconds_between_times("08:30:00", "15:45:30")) # (7, 15, 30)
print(utils.time_until_date("2024-05-27 23:59:59")) # Remaining days, hours, minutes, seconds
print(utils.time_add_days_and_format("2024-05-01", 30)) # "2024-05-31 (Friday)"
print(utils.time_is_weekend("2024-05-25")) # True
print(utils.time_is_leap_year(2024)) # True
print(utils.time_days_in_month(2024, 2)) # 29
print(utils.time_next_weekday("2024-05-25", 0)) # 2024-05-27
print(utils.time_since("2022-01-01 00:00:00")) # (2, 4, 24, 14, 30, 15)
print(utils.time_business_days_between_dates("2024-05-01", "2024-05-25")) # 17