-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 1
Open
Description
Author:ProZoom
Hobby:爱折腾、爱思考,想静静的ProZoom
Github --- 简书 --- CSDN --- 关于我
基本语法
注释
kotlin和java、JS一样,支持行注释和块注释
//行注释
/*
* 块注释
*/定义包
和Java一样,包的声明处于源文件顶部
package prozoom
import java.util.*定义函数
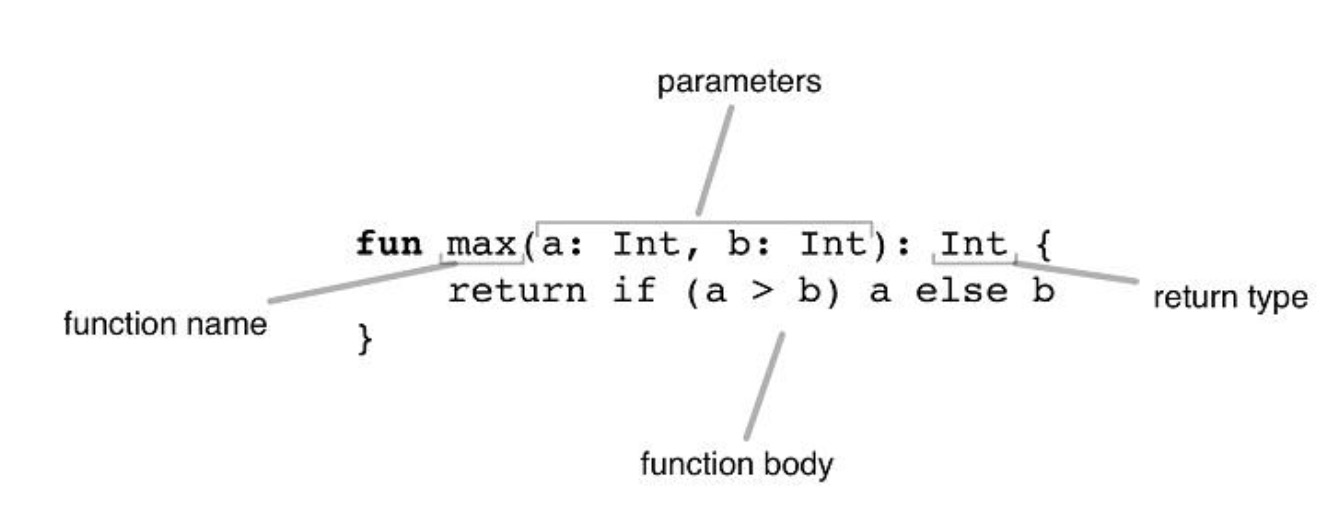
- 带有两个Int参数,返回Int的函数:
fun max(a: Int, b: Int): Int {
if (a > b)
return a
else
return b
//return if (a>b) a else b
}- 将表达式作为函数体,返回值类型自动推断的函数:
fun max(a: Int, b: Int)= if (a > b) a else b
- 函数返回无意义的值:
fun printSum(a: Int, b: Int): Unit {
println("sum of $a and $b is ${a + b}")
}- Uint 返回类型可以忽略:
fun printSum(a: Int, b: Int) {
println("sum of $a and $b is ${a + b}")
}定义局部变量
- 只读(不可变)的局部变量:
val str = "The Ultimate Question of Life, the Universe, and Everything"
val a = 42
val b: Int = 42
val c = 7.5e4 // 7.5*10000
val d: Int
d = 43 - 可变变量:
var a:Int = 23
a = 32字符串模版
var a = 1
// 模板中的简单名称:
val s1 = "a is $a"
a = 2
// 模板中的任意表达式:
val s2 = "${s1.replace("is", "was")}, but now is $a"
println(s2)
//输出:a was 1, but now is 2
使用可空值及Null检测
当某个变量的值可以为 null 的时候,必须在声明处的类型后添加 ? 来标识该引用可为空。
如果 str 的内容不是数字返回 null:
fun parseInt(str: String): Int? {
// ……
}使用返回可空值的函数:
fun printProduct(arg1: String, arg2: String) {
val x = parseInt(arg1)
val y = parseInt(arg2)
// 直接使用 `x * y` 可能会报错,因为他们可能为 null
if (x != null && y != null) {
// 在空检测后,x 和 y 会自动转换为非空值(non-nullable)
println(x * y)
}
else {
println("either '$arg1' or '$arg2' is not a number")
}
}使用类型检测及自动类型转换
is 运算符检测一个表达式是否某类型的一个实例。
如果一个不可变的局部变量或属性已经判断出为某类型,那么检测后的分支中可以直接当作该类型使用,无需显式转换:
fun getStringLength(obj: Any): Int? {
if (obj is String) {
// `obj` 在该条件分支内自动转换成 `String`
return obj.length
}
// 在离开类型检测分支后,`obj` 仍然是 `Any` 类型
return null
}使用for循环
val items = listOf("apple", "banana", "kiwi")
for (item in items) {
println(item)
}
输出:
apple
banana
kiwi
val items = listOf("apple", "banana", "kiwi")
for (index in items.indices) {
println("item at $index is ${items[index]}")
}
输出:
item at 0 is apple
item at 1 is banana
item at 2 is kiwi使用while循环
val items = listOf("apple", "banana", "kiwi")
var index = 0
while (index < items.size) {
println("item at $index is ${items[index]}")
index++
}
输出:
item at 0 is apple
item at 1 is banana
item at 2 is kiwi使用when表达式
fun describe(obj: Any): String =
when (obj) {
1 -> "One"
"Hello" -> "Greeting"
is Long -> "Long"
!is String -> "Not a string"
else -> "Unknown"
}使用区间(range)
//打印1~100
for (i in 1..100) {
println(i)
}
//打印1-10,步进为2
for (x in 1..10 step 2) {
print(x)
}
//打印100-1,步进为10
for (i in 100 downTo 1 step 10) {
println(i)
}
使用集合
对集合进行迭代:
for (item in items) {
println(item)
}使用 in 运算符来判断集合内是否包含某实例:
when {
"orange" in items -> println("juicy")
"apple" in items -> println("apple is fine too")
}使用 lambda 表达式来过滤(filter)和映射(map)集合:
fruits
.filter { it.startsWith("a") }
.sortedBy { it }
.map { it.toUpperCase() }
.forEach { println(it) }习惯用法
函数的默认参数
fun foo(a: Int = 0, b: String = ""){
……
}list过滤
val positives = list.filter { x -> x > 0 }or
val positives = list.filter { it > 0 }String内插
val name="ProZoom"
println("Name $name")遍历map/pair型list
for ((k, v) in map) {
println("$k -> $v")
}k、v 可以改成任意名字。
使用区间(range)
for (i in 1..100) { …… } // 闭区间:包含 100
for (i in 1 until 100) { …… } // 半开区间:不包含 100
for (x in 2..10 step 2) { …… }
for (x in 10 downTo 1) { …… }
if (x in 1..10) { …… }只读 list
val list = listOf("a", "b", "c")只读 map
val map = mapOf("a" to 1, "b" to 2, "c" to 3)
访问 map
println(map["key"])
map["key"] = value延迟属性
val p: String by lazy {
// 计算该字符串
}扩展函数
fun String.spaceToCamelCase() { …… }
"Convert this to camelcase".spaceToCamelCase()
创建单例
object Resource {
val name = "Name"
}
返回 when 表达式
fun transform(color: String): Int {
return when (color) {
"Red" -> 0
"Green" -> 1
"Blue" -> 2
else -> throw IllegalArgumentException("Invalid color param value")
}
}“try/catch”表达式
fun test() {
val result = try {
count()
} catch (e: ArithmeticException) {
throw IllegalStateException(e)
}
// 使用 result
}“if”表达式
fun foo(param: Int) {
val result = if (param == 1) {
"one"
} else if (param == 2) {
"two"
} else {
"three"
}
}编码规范
命名风格
默认使用Java的编码规范,比如:
- 使用驼峰法命名(并避免命名含有下划线)
- 类型名以大写字母开头
- 方法和属性以小写字母开头
- 使用 4 个空格缩进
- 公有函数应撰写函数文档,这样这些文档才会出现在 Kotlin Doc 中
Reactions are currently unavailable